Pressure-Based Gain Factor Control for Mobile 3D Interaction using Locally-Coupled Devices
Description:
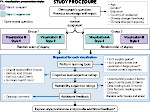
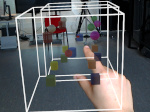
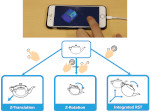
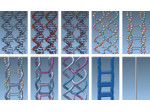
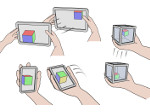
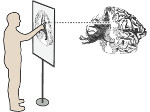
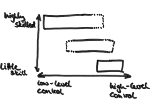
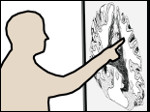
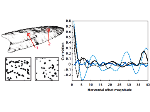
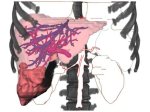
We present the design and evaluation of pressure-based interactive control of 3D navigation precision. Specifically, we examine the control of gain factors in tangible 3D interactions using locally-coupled mobile devices. By focusing on pressure as a separate input channel we can adjust gain factors independently from other input modalities used in 3D navigation, in particular for the exploration of 3D visualizations. We present two experiments. First, we determined that people strongly preferred higher pressures to be mapped to higher gain factors. Using this mapping, we compared pressure with rate control, velocity control, and slider-based control in a second study. Our results show that pressure-based gain control allows people to be more precise in the same amount of time compared to established input modalities. Pressure-based control was also clearly preferred by our participants. In summary, we demonstrate that pressure facilitates effective and efficient precision control for mobile 3D navigation.
Paper download:  (5.5 MB)
(5.5 MB)
Demo/Source Code:
You can get the code on Github for the tablet app (Android, requires Google Tango tablet with the special pressure sensing hardware prototype).
Videos:
Get the videos:
- download the paper video (720, MPEG4, 47.1MB),
- watch the paper video on YouTube.
- watch the conference preview video on YouTube.
Pictures:
Main Reference:
Other Reference:
| Lonni Besançon (2017) An Interaction Continuum for 3D Data Visualization. PhD thesis, Université Paris-Saclay, France, December 2017. | | ||
This work was done at the AVIZ project group of Inria, France, in collaboration with the LIMSI lab at CNRS, France.